Biological Catalysts
Biological Catalysts: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Enzymes, Active Site of Enzymes, Forensic Technologies, Relation between Forensics and Salivary Amylase, Metabolic Reactions, Naming Enzymes & Lock and Key Hypothesis etc.
Important Questions on Biological Catalysts
The metabolic reaction takes place both in vitro and in vivo condition.
The positive result of the presence of salivary amylase clearly prove that a person was involved in a particular scene.
Which of the following matches between digestive enzyme and molecule digested is incorrect?
Which of the following scientist has proposed the Lock and Key hypothesis?
Why microbial enzymes are used instead of chemical catalysts in the chemical industry?
Identify the correct pair/s:
Enzymes - Nutrients they digest
Active site is the part of an enzyme molecule to which the substrate temporarily binds.
Today, forensic scientists are also able to search for cheek cells within a saliva sample.
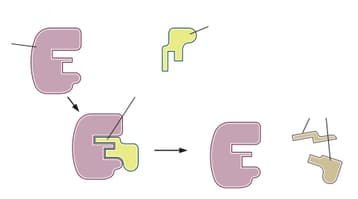
Choose correct statement with respect to 'The lock and key mechanism':
Trypsin is a serine protease found in the digestive system of many vertebrates.
_____ is a presumptive test used in forensic science examinations for the detection of areas of possible saliva staining.
Mention the applications of forensic technologies is
What is the function of malate dehydrogenase during the aerobic reaction?
Which enzyme performs the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide?
